Tools
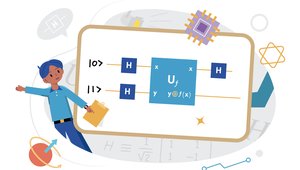
Quantum Circuit Simulator
Design, visualize, and run your own quantum circuits here. The tool can also generate a Qibo code to be run on your own machine.
You can learn about quantum circuits here:
What does each gate do:
 Hadamard gate. Creates an equal superposition state in the computational basis
Hadamard gate. Creates an equal superposition state in the computational basis Pauli-X gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the X-axis of the Bloch sphere
Pauli-X gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the X-axis of the Bloch sphere Pauli-Y gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere
Pauli-Y gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere Pauli-Z gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere
Pauli-Z gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere Control gate. This gate sets the control qubit of a control operation. Needs to be paired with another single-qubit gate
Control gate. This gate sets the control qubit of a control operation. Needs to be paired with another single-qubit gate  Phase gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Phase gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle T gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
T gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle SWAP gate. Interchanges the states of two qubits. Needs to be applied to two qubits
SWAP gate. Interchanges the states of two qubits. Needs to be applied to two qubits Arbitrary unitary gate. A general single-qubit transformation through rotations and phase shifts
Arbitrary unitary gate. A general single-qubit transformation through rotations and phase shifts Measurement operator. Collapses a qubit’s state onto the computational basis
Measurement operator. Collapses a qubit’s state onto the computational basis
 Hadamard gate. Creates an equal superposition state in the computational basis
Hadamard gate. Creates an equal superposition state in the computational basis Pauli-X gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the X-axis of the Bloch sphere
Pauli-X gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the X-axis of the Bloch sphere Pauli-Y gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere
Pauli-Y gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere Pauli-Z gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere
Pauli-Z gate. Applies a 180° rotation around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere Control gate. This gate sets the control qubit of a control operation. Needs to be paired with another single-qubit gate
Control gate. This gate sets the control qubit of a control operation. Needs to be paired with another single-qubit gate  Phase gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Phase gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle T gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
T gate. Rotates a qubit’s phase around the Z-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle SWAP gate. Interchanges the states of two qubits. Needs to be applied to two qubits
SWAP gate. Interchanges the states of two qubits. Needs to be applied to two qubits Arbitrary unitary gate. A general single-qubit transformation through rotations and phase shifts
Arbitrary unitary gate. A general single-qubit transformation through rotations and phase shifts Measurement operator. Collapses a qubit’s state onto the computational basis
Measurement operator. Collapses a qubit’s state onto the computational basis